OutputStream Classes
Introduction
-
OutputStreamis an abstract class used to write byte-oriented data to output destinations like files, memory or network connections. -
It is present in
java.iopackage. -
It provides basic methods like
write()to send data to output destinations.
-
Below is the diagram for OutputStream class hierarchy:
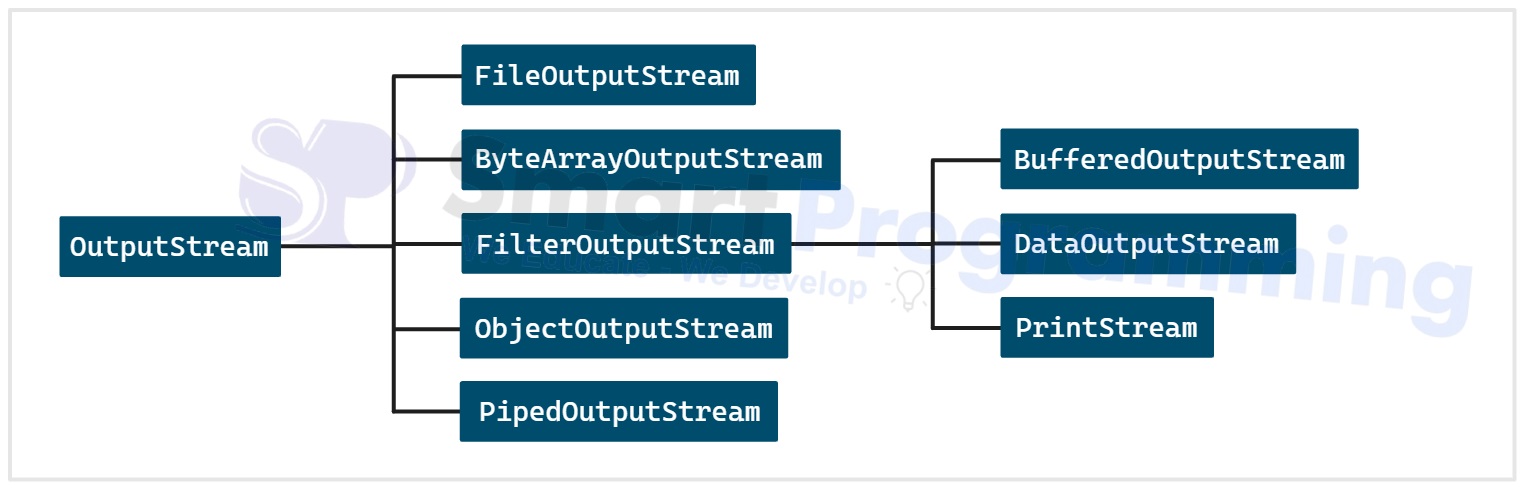
- Each of these classes are designed for specific purposes, which are explained below one by one.
1. FileOutputStream
- Description: Writes data to a file in the form of bytes.
- Use in Projects: Useful for writing binary data like images, audio etc.
-
Example Syntax:
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("output.txt"); fos.write(65); // writes 'A'
2. ByteArrayOutputStream
- Description: Writes data to a byte array in memory.
- Use in Projects: Useful for temporary storage or manipulating byte data before writing to a file.
-
Example Syntax:
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); baos.write(65); byte[] data = baos.toByteArray();
3. FilterOutputStream
- Description: A base class for other output stream filters (not used directly).
- Use in Projects: Extended by classes like BufferedOutputStream, DataOutputStream, PrintStream.
-
Example Syntax:
Rarely used directly. Mostly used via subclasses.
4. BufferedOutputStream
- Description: Adds buffering to output stream for faster writing.
- Use in Projects: Useful when writing large files (improves performance).
-
Example Syntax:
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("file.txt")); bos.write(65);
5. DataOutputStream
- Description: Writes Java primitive data types (int, float, double, etc.) in a machine-independent way.
- Use in Projects: Useful for binary files containing structured primitive data.
-
Example Syntax:
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.bin")); dos.writeInt(123);
6. PrintStream
- Description: Prints data to an output stream in a readable text form (includes methods like print(), println()).
- Use in Projects: Useful for logging, console-like output, or text-based file output.
-
Example Syntax:
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("log.txt")); ps.println("Hello World");
7. ObjectOutputStream
- Description: Writes Java objects to a stream for storage or transmission.
- Use in Projects: Used for serialization.
-
Example Syntax:
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("object.ser")); oos.writeObject(new MyClass());
8. PipedOutputStream
- Description: Writes data that can be read by a connected PipedInputStream.
- Use in Projects: Useful for communication between threads.
-
Example Syntax:
PipedOutputStream pos = new PipedOutputStream(); PipedInputStream pis = new PipedInputStream(pos); pos.write(65);
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



