InputStream Classes
Introduction
-
InputStreamis an abstract class used to read byte-oriented data from input sources such as files, memory or network connections. -
It is present in
java.iopackage. -
It provides basic methods like
read()to read data from input sources.
-
Below is the diagram for InputStream class hierarchy:
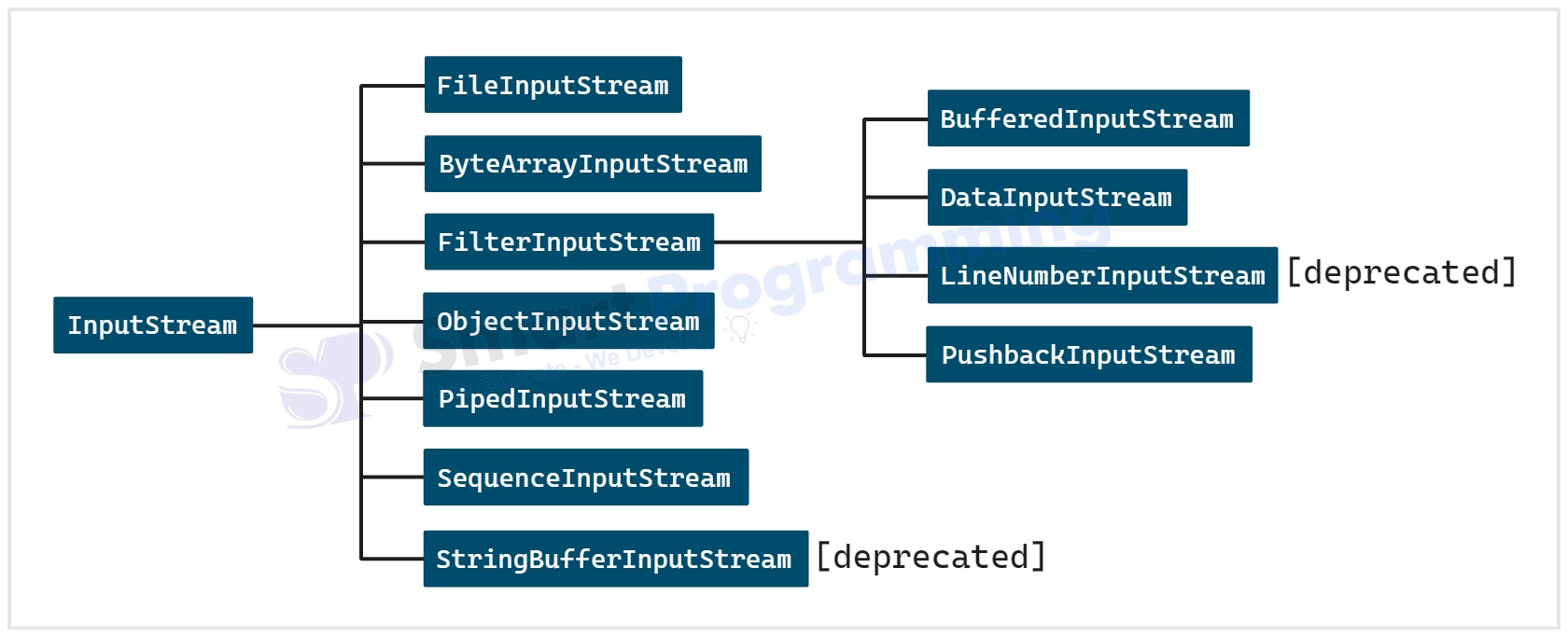
- Each of these classes are designed for specific purposes, which are explained below one by one.
1. FileInputStream
- Description: Reads data from a file in the form of bytes.
- Use in Projects: Useful for reading binary files such as images, audio, or video.
-
Example Syntax:
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("file.txt"); int data = fis.read(); fis.close();
2. ByteArrayInputStream
- Description: Reads data from a byte array as an input stream.
- Use in Projects: Useful for testing, or when data is already available in memory (like byte arrays).
-
Example Syntax:
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("file.txt"); int data = fis.read(); fis.close();
3. FilterInputStream
- Description: A base class for other input stream filters (not used directly).
- Use in Projects: Extended by classes like BufferedInputStream, DataInputStream, etc.
-
Example Syntax:
Rarely used directly. Mostly used via subclasses.
4. BufferedInputStream
- Description: Adds buffering to input stream for faster reading.
- Use in Projects: Useful when reading large files (improves performance).
-
Example Syntax:
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("file.txt")); int b = bis.read();
5. DataInputStream
- Description: Reads Java primitive data types (int, float, double, etc.) in a machine-independent way.
- Use in Projects: Useful when working with binary data containing primitive types.
-
Example Syntax:
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.bin")); int num = dis.readInt();
6. LineNumberInputStream
- Description: Deprecated because its functionality is replaced by LineNumberReader.
- Use in Projects: Should not be used in modern code.
7. PushbackInputStream
- Description: Allows a byte to be pushed back into the stream, so it can be read again.
- Use in Projects: Useful in parsers or compilers.
-
Example Syntax:
PushbackInputStream pbis = new PushbackInputStream(new FileInputStream("file.txt")); int b = pbis.read(); pbis.unread(b);
8. ObjectInputStream
- Description: Reads Java objects that were written using ObjectOutputStream.
- Use in Projects: Used for deserialization.
-
Example Syntax:
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.ser")); MyClass obj = (MyClass) ois.readObject();
9. PipedInputStream
- Description: Reads data written to a connected PipedOutputStream.
- Use in Projects: Useful for communication between threads.
-
Example Syntax:
PipedInputStream pis = new PipedInputStream(); PipedOutputStream pos = new PipedOutputStream(pis); pos.write(65); int b = pis.read(); // reads 'A'
10. SequenceInputStream
- Description: Reads data sequentially from multiple input streams as if they were a single stream.
- Use in Projects: Useful for merging multiple files into one.
-
Example Syntax:
SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream( new FileInputStream("a.txt"), new FileInputStream("b.txt") );
11. StringBufferInputStream
- Description: Deprecated because it does not properly convert characters to bytes. Use StringReader instead.
- Use in Projects: Should not be used in modern code.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



