Serialization and Deserialization
Introduction
- In Java, serialization and deserialization is a key concept used frequently in real-world applications, even though we may not always realize it.
-
Serialization:
- It is the process of converting an object into a byte stream so that it can be easily stored in files, memory or databases or transmitted over a network.
-
In Java, serialization is done using the
ObjectOutputStreamclass.
-
Deserialization:
- It is the reverse process of serialization. It involves converting the byte stream back into an object.
-
In Java, deserialization is done using the
ObjectInputStreamclass.
-
Diagram:
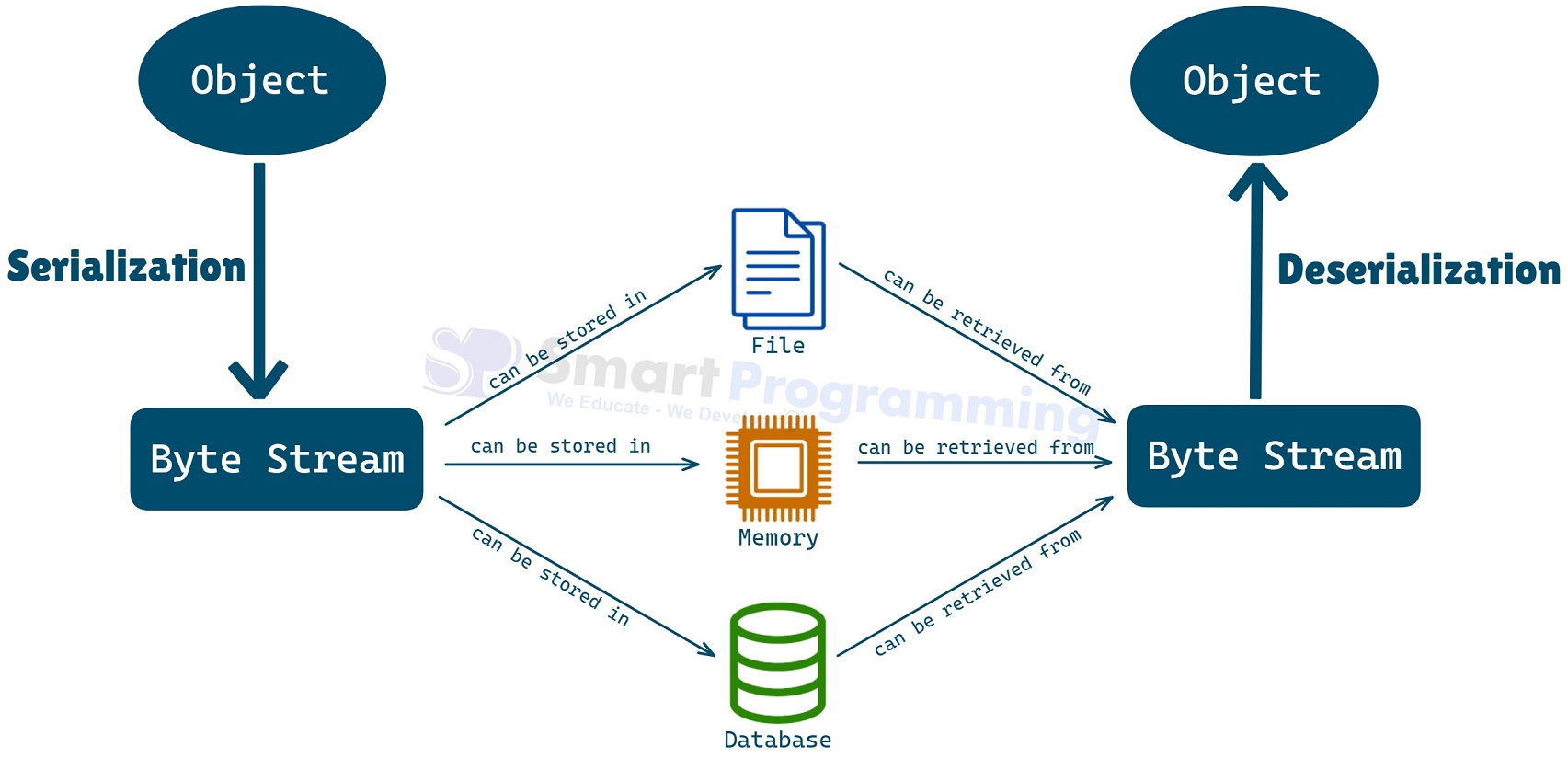
Advantages of Serialization:
-
Object Persistence:
- Serialization allows objects to be saved to files or databases, enabling the persistence of their state.
-
Data Transfer:
- It helps in sending objects over a network by converting them into a byte stream that can be easily transmitted.
-
Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- Serialized objects can be transferred between different platforms or systems without compatibility issues since the byte stream format is platform-independent.
-
Caching:
- Serialization helps in storing objects in memory or on disk for efficient access, reducing redundant calculations or database queries.
-
Backup and Restore:
- Serialized objects can be backed up in a file and restored later, ensuring that the state of an application is preserved.
Advantages of Deserialization:
-
Reconstruction of Objects:
- Deserialization enables the recreation of objects from byte streams, restoring their original state and allowing continued use.
-
Data Retrieval:
- It allows objects to be retrieved from a file, memory, or database, enabling an application to resume its state after a restart or network transfer.
-
Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- Just like serialization, deserialization ensures that objects can be read and used across different platforms, making the system more flexible.
-
Session Management:
- Helps in restoring user sessions by deserializing session data that was serialized earlier, providing a seamless experience.
Serialization & Deserialization Program:
-
We have one Student class, we will create an object of Student class and serialize and deserialize it.
import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable { // Define the instance variables private String name; private int rollno; // Constructor to initialize the variables public Student(String name, int rollno) { this.name = name; this.rollno = rollno; } // Getters for the variables public String getName() { return name; } public int getRollno() { return rollno; } // Displaying student details public void display() { System.out.println("Name: " + name); System.out.println("Roll No: " + rollno); } } -
Now we will serialize Student class object using
ObjectOutputStreamclass as follows:import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class SerializationExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a Student object Student student = new Student("Deepak", 101); // Serialize the object try ( FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("student.ser"); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut) ) { out.writeObject(student); // Serialize the student object System.out.println("Student object has been serialized."); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }Output:
Student object has been serialized.
-
Now, we will deserialize Student object using
ObjectInputStreamclass as follows:import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class DeserializationExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // Deserialize the object try ( FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream("student.ser"); ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fileIn) ) { Student student = (Student) in.readObject(); // Deserialize the object System.out.println("Student object has been deserialized."); student.display(); // Display the student details } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }Output:
Student object has been deserialized. Name: Deepak Roll No: 101
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



