Byte Stream in Java IO
Introduction
- A byte stream is a flow of data that handles input and output of data in bytes (8-bit units).
-
Byte streams are used for performing low-level input and output operations on various types of data, such as:
- Text files
-
Images (
.jpg,.png) -
Audio (
.mp3) -
Video (
.mp4) -
Executables (
.exe)
-
How Byte Stream Works?
-
Byte streams transfer data in binary form, i.e.,
0and1. - Each byte represents 8 bits of data.
- This allows the program to read/write any type of file (text or non-text) because it deals directly with the binary representation.
-
Example:
-
Reading a text file:
H→01001000 - Reading an image file: binary data directly transferred as bytes.
-
Reading a text file:
-
Byte streams transfer data in binary form, i.e.,
Hierarchy of Byte Streams:
-
Byte streams in Java are divided into two main categories:
-
InputStream(for reading bytes) -
OutputStream(for writing bytes)
-
-
Below is the hierarchy:-
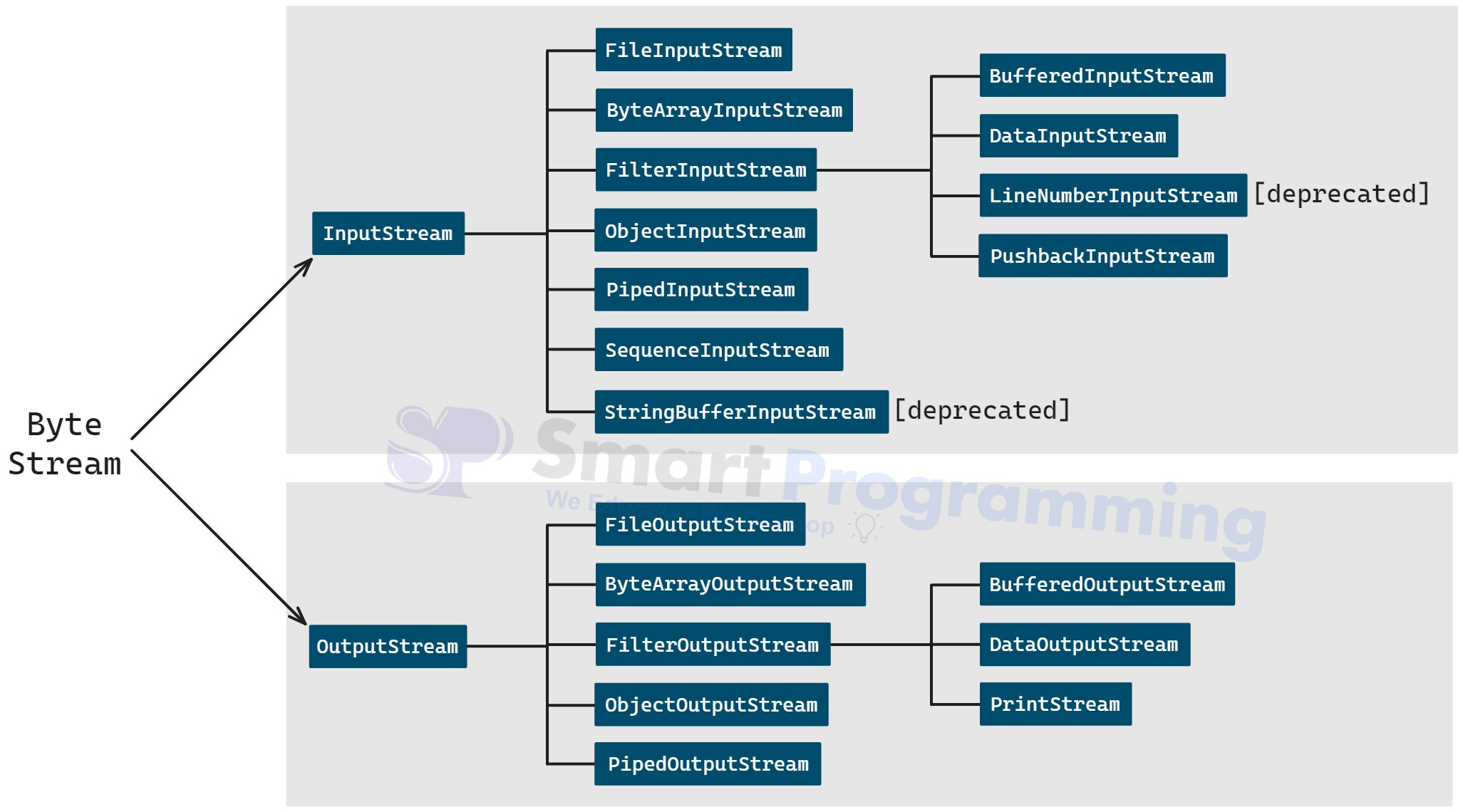
-
The
read()method is common to allInputStreamclasses, and thewrite()method is common to allOutputStreamclasses. Together, they form the basic building blocks of byte stream I/O in Java.
Program for InputStream (FileInputStream):
- Below is the program to read file:
-
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class ReadFileExample { public static void main(String[] args) { try { // Open file for reading FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d://aaa.txt"); int i; System.out.println("----- Reading data from file -----"); while ((i = fis.read()) != -1) { System.out.print((char) i); // convert byte to char } fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("Error reading file: " + e.getMessage()); } } } -
Make sure that there should be
aaa.txtfile in D drive (d://).
Program for OutputStream (FileOutputStream):
- Below is the program to write text in file:
-
import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class WriteFileExample { public static void main(String[] args) { try { // Open file for writing FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d://bbb.txt"); String data = "Hello, this is my first Java Program to write data in file...."; fos.write(data.getBytes()); // write string as bytes fos.close(); System.out.println("Data successfully written to output.txt"); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("Error writing file: " + e.getMessage()); } } } - Make sure that the path provided should be correct.
- Click here to read all the InputStream classes deeply.
- Click here to read all the OutputStream classes deeply.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



