Collections Framework in Java
Introduction
-
The Java Collections Framework consists of two main terms:
-
Collections:
- A Collection is a single entity that stores multiple elements as a single unit.
- Examples: List of students, set of employee IDs, map of country & capital.
-
Framework:
- A Framework is a set of classes and interfaces that provide a consistent and reliable way to perform data handling operations.
- Examples: Java I/O Framework, Java Concurrency Framework (Multithreading), Java Stream API (Java 8 onwards), JDBC API (Java Database Connectivity) etc.
-
Collections:
- Definition: The Collections Framework is a unified architecture for representing and manipulating collections.
-
It provides:
-
Interfaces – e.g.,
List,Set,Queue,Mapetc. -
Implemented Classes – e.g.,
ArrayList,HashSet,HashMapetc. -
Algorithms – e.g., sorting, searching, and shuffling provided by the
Collectionsclass.
-
Interfaces – e.g.,
- Its main goal is to make data manipulation in Java easy, efficient, and standardized.
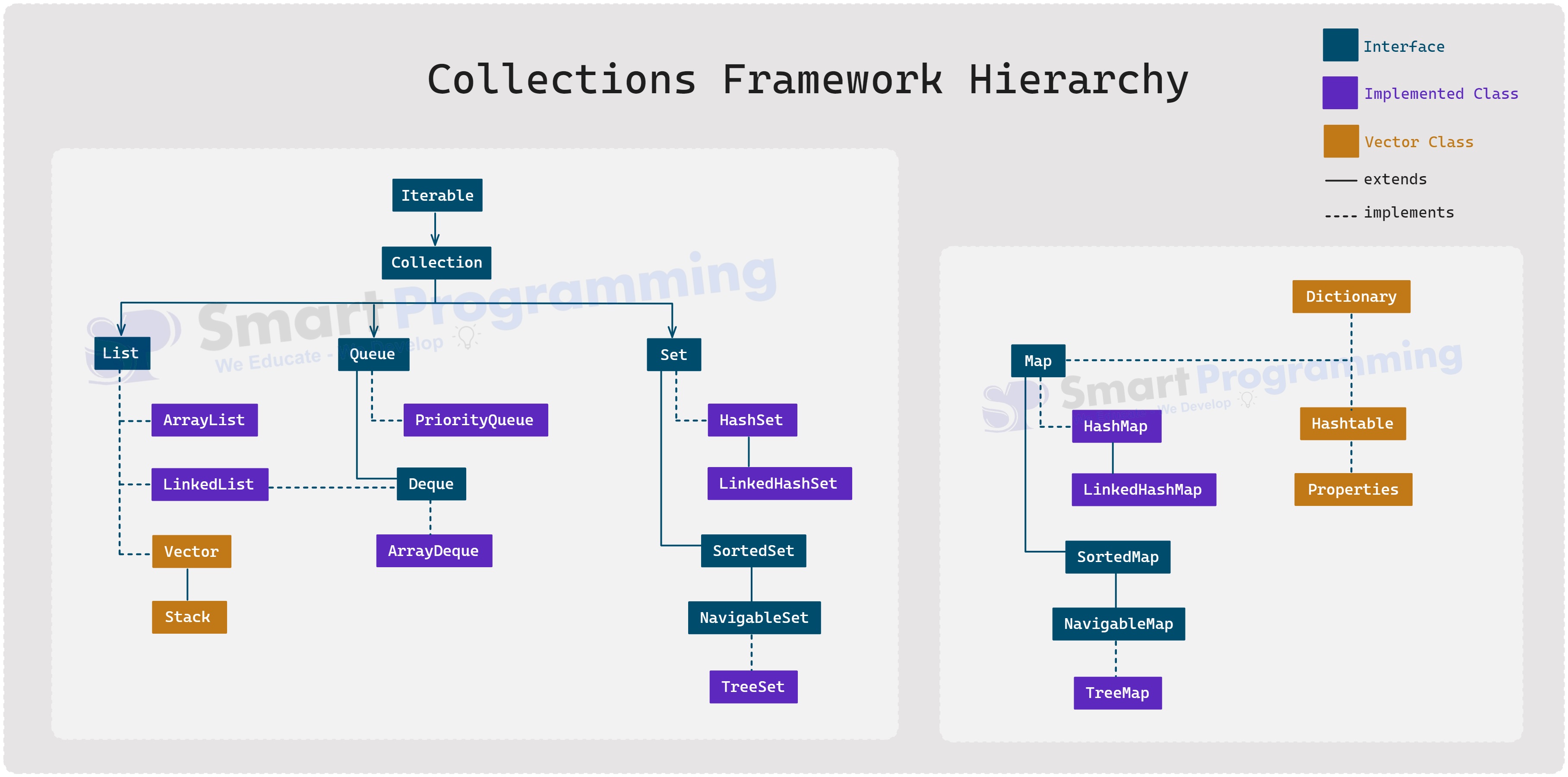
Hierarchy of Collections Framework
-
The Collections Framework in Java contains two main interfaces:
-
Collection– Represents a group of objects, like List, Set, or Queue. -
Map– Represents a collection of key-value pairs.-
Note:
Mapdoes not extendCollection.
-
Note:
-
-
Below is the hierarchy of the Collections Framework in Java:
-
Tip: Some classes like
Vector,Stack,Hashtable,Properties, andDictionaryare considered legacy classes but are still part of the framework for backward compatibility. -
The two main packages present in Collections Framework are:-
-
java.util.Collectionpackage -
java.util.Mappackage
-
Uses of Collections Framework
-
Storing Data:
- Use
ArrayListorLinkedListto store lists of students, products, or items.
- Use
-
Processing Queues:
- Use
QueueorDequefor tasks like managing print jobs or task scheduling.
- Use
-
Managing Unique Data:
- Use
HashSetorTreeSetto store unique elements like employee IDs.
- Use
-
Key-Value Mapping:
- Use
HashMaporTreeMapto store data in key-value pairs like country-capital mapping.
- Use
-
Sorting and Searching:
- Collections classes provide built-in methods for sorting, searching, and shuffling data easily.
Advantages of Collections Framework
-
Reusability:
- You can use predefined classes like
ArrayList,HashMap, etc., without writing code from scratch.
- You can use predefined classes like
-
Efficiency:
- Collections classes are optimized for storing, retrieving, and manipulating data quickly.
-
Consistency:
- Provides a standard way to work with data structures, so code is easier to read and maintain.
-
Flexibility:
- Supports different types of collections like
List,Set,Mapfor various needs.
- Supports different types of collections like
-
Thread-Safety (optional):
- Some collections like
VectorandHashtableare synchronized and safe for multithreaded use.
- Some collections like
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



