Data Types in Java
Introduction
- In Java, when we provide data like 101, Deepak, 91.4, etc., we need to specify that which type of data we are providing.
- For example, we need to specify that 101 is of type int, Deepak is of type String, and 91.4 is of type float or double.
- So, we can say that in Java, every piece of data has a specific type, known as a "data type".
-
Purpose of Data Types :
-
Data types inform the compiler about the kind of data to be stored in a variable.
For example: Declaring int rollno = 101; tells the compiler that rollno will store an integer. -
They help allocate the necessary memory for that data, ensuring that the program uses memory efficiently and that data is stored and processed correctly.
For example: int rollno allocates 4 bytes of memory, same float marks will also store 4 bytes of memory.
-
Data types inform the compiler about the kind of data to be stored in a variable.
-
Data Types & Variables :
- Data is stored in variables, and each variable is assigned a specific data type.
- A variable's data type determines what kind of value it can hold and what operations can be performed on it.
-
For example :
int rollno = 101; // "int" is "data type" // "rollno" is "variable" // "101" is "literal' or "data" (value assigned to the variable)
-
Diagram :

Types of Data Types
-
There are 2 types of Data Types in Java which are as below :-
- Primitive Data Types
- Non - Primitive Data Types
-
Below is the diagram representing the data types in java....
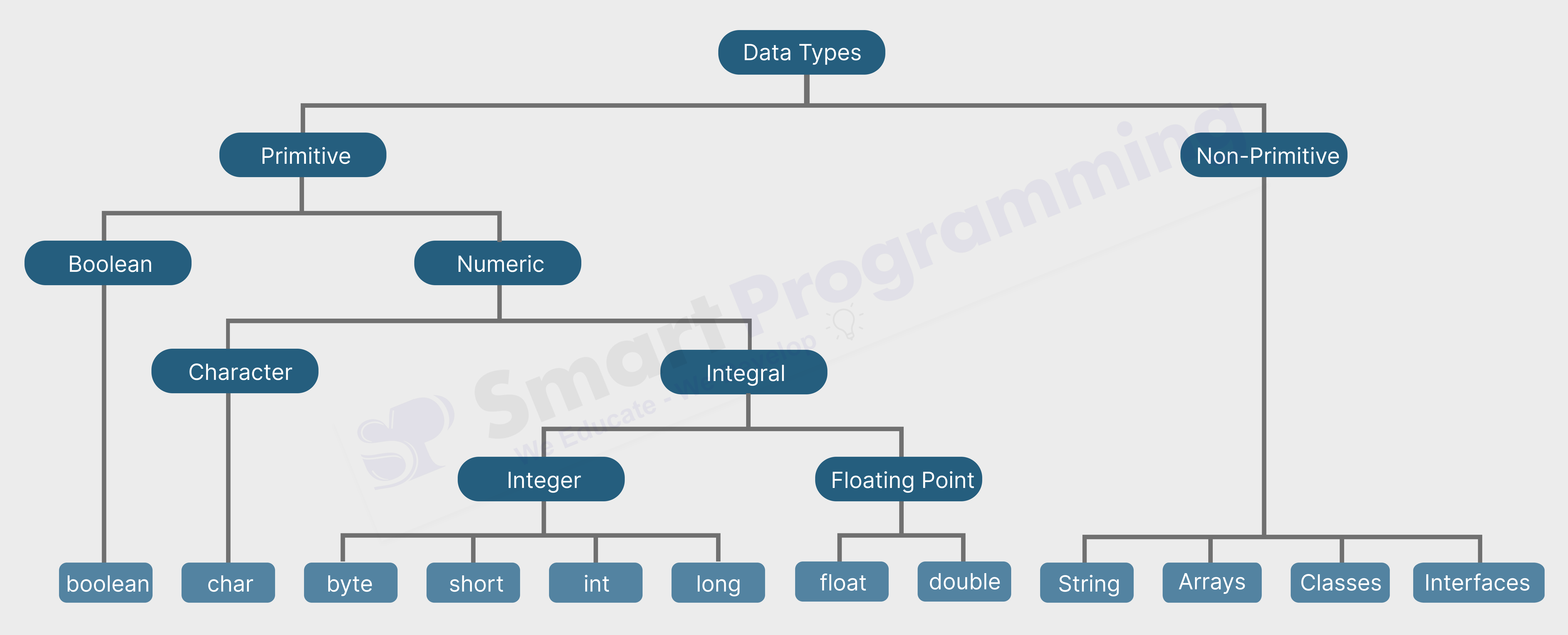
1. Primitive Data Types
- Primitive data types are pre-defined data types.
- There are total 8 primitive data types in Java i.e. boolean, char, byte, short, int, long, float and double.
- Primitive data types have fixed memory sizes for example char always occupies 2 byte of memory, int occupies 4 byte of memory etc.
- Click here to read primitive data types more deeply.
2. Non-Primitive Data Types
- Non-Primitive data types are user-defined or derived data types.
- Non-Primitive data types examples are Strings, Arrays, classes, interfaces etc.
- Non-Primitive data types does'nt have fixed memory sizes, they depends on the data or objects they reference.
For example, a String object’s memory usage depends on the string's length. - Click here to read non-primitive data types more deeply.
Click Here to see the difference between Primitive Data Types & Non-Primitive Data Types.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



