Merging Branches in Git Repository - git merge
Introduction
-
git mergecommand is used to combine the work from one branch into another, typically during development. -
The most common use case is merging a feature branch (like
feature-xyz) into a main or development branch. - It’s commonly used in collaborative environments when feature branches are finished and ready to be integrated into the main branch.
- Merging keeps the full history of changes from both branches.
NOTE :
-
This is different from
rebase, which rewrites history to make a cleaner linear flow.
-
There are two types of merges:
- Fast-forward merge: Happens when the current branch has not diverged from the target branch.
- Three-way merge: Happens when both branches have diverged — Git creates a new merge commit.
How to use git merge ?
- Open the Git terminal (or command prompt) and navigate to the project folder where your Git repository is initialized.
-
Create and Commit on a Feature Branch :-
-
Let’s assume you're on the default branch (main) and want to work on a new feature.
-
Create a new branch (if not created):
-
git branch feature-1
-
-
Switch to the new branch:
-
git switch feature-1
-
-
Make changes to your files, then add and commit them:
-
git add . -
git commit -m "Implemented feature-1"
-
-
Create a new branch (if not created):
-
Below are the commands with output:
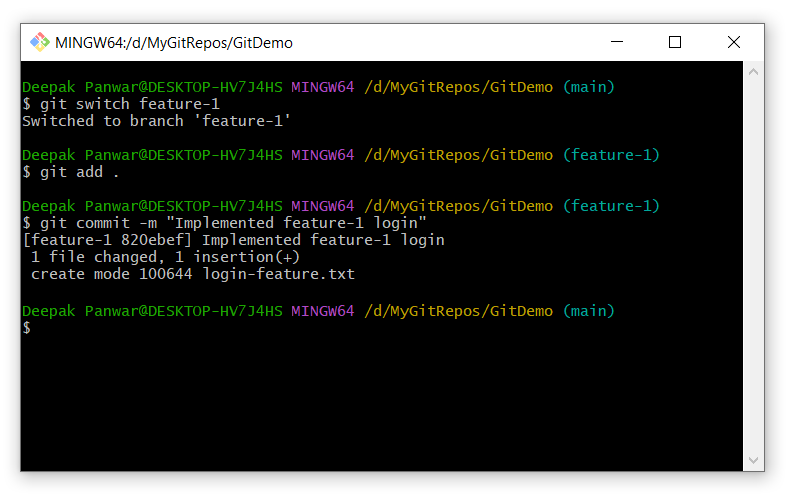
-
Let’s assume you're on the default branch (main) and want to work on a new feature.
-
Switch Back to the Main Branch :-
-
Once your work on
feature-1is complete, switch back to themainbranch: -
-
git switch main
-
-
Once your work on
-
Merge the Feature Branch into Main
-
Now, merge the
feature-1branch intomain-
git merge feature-1-
The git merge command always merges the specified branch (i.e.
feature-1) into your current branch (i.e.main). - If there are no conflicts, Git will create a merge commit automatically.
-
If there are conflicts, resolve them manually in the files. Then:
-
git add . -
git commit
-
-
The git merge command always merges the specified branch (i.e.
-
-
Now, merge the
-
(Optional) Delete the Feature Branch
- After successful merging, you can delete the feature branch:
-
git branch -d feature-1
-
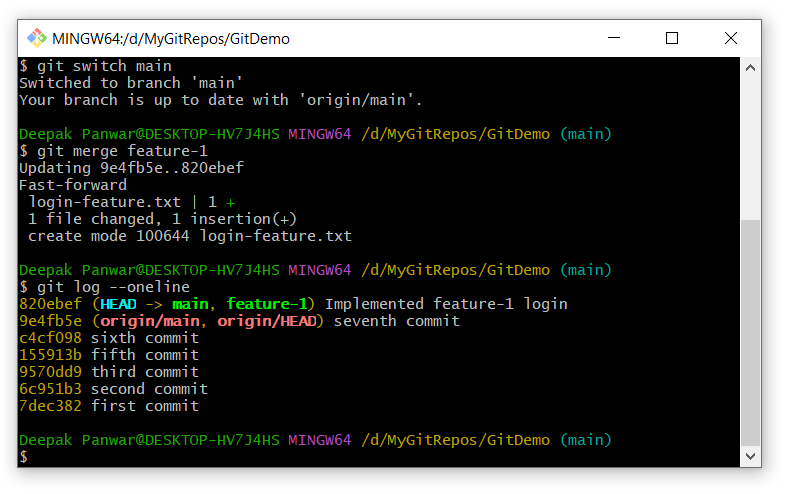
Verify the Merge
-
Use this to check the branch list and confirm you’re on
main-
git branch
-
-
And view the merge history:
-
git log --oneline
-
-
Use this to check the branch list and confirm you’re on
-
Below is the output of the above commands:
-
Different ways to use git merge ?
-
Merging a Local Branch into the Current Branch:
-
Syntax :
-
git merge <branch-name>
-
-
Example:
git merge feature-branch
-
Merges
feature-branchinto the currently checked-out branch.
-
Syntax :
-
Abort a Merge in Case of Conflict:
-
Syntax :
-
git merge --abort
-
- If conflicts occur during merging, this command cancels the merge process.
-
Syntax :
-
Merging After Fetching from a Remote Repository (Most Common):
-
Syntax :
-
git merge origin/<branch-name>
-
-
Example :
-
git merge origin/main
-
-
Merges the latest changes from the remote
mainbranch into your local branch after fetching updates.
-
Syntax :
-
Fast-Forward Merge (If No Diverging Changes Exist) (Commonly Used) :
-
Syntax :
-
git merge --ff-only <branch-name>
-
-
Exmaple :
-
git merge --ff-only origin/main
-
- Merges the remote branch only if no conflicting changes exist.
-
Syntax :
-
Squash Merge (Combine Multiple Commits into One Before Merging) (Commonly Used for Clean History) :
-
Syntax :
-
git merge --squash <branch-name>
-
-
Example :
-
git merge --squash feature-branch
-
-
Combines all commits from
feature-branchinto a single commit before merging.
-
Syntax :
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.