Connecting & Managing Repositories - git remote
Introduction
-
git remotecommand is used to manage remote connections in a Git project. - A remote is a version of your project that is hosted on the internet or another network — commonly on platforms like GitHub, GitLab or Bitbucket.
-
What does
git remotedo ?- Lists all the remote repositories connected to your local Git project.
- Allows you to add, remove, rename and inspect remote repositories.
- Helps you collaborate with others by pushing to or pulling from remote repositories.
How to use git remote ?
-
Open the Git terminal (or command prompt) and navigate to the project folder where your Git repository is initialized.
-
Check Existing Remote Repositories:
-
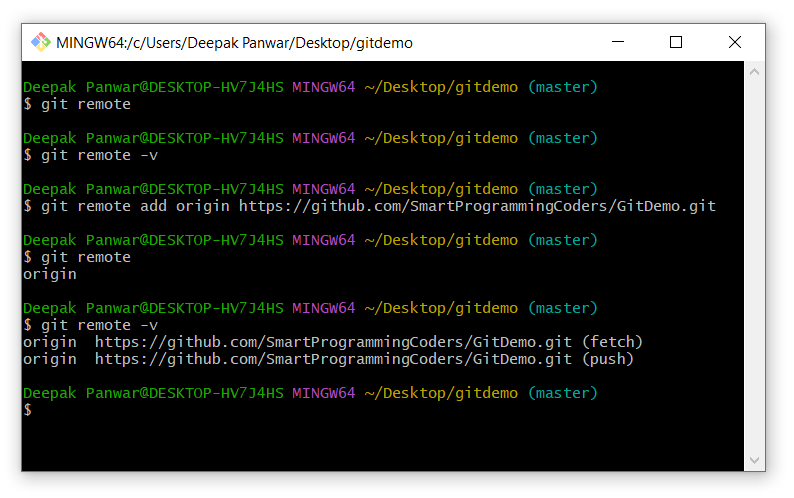
git remote- It will show the names of all connected remotes (e.g., origin).
-
git remote -v- It will display the URLs of the remotes along with their fetch/push information.
-
-
Add GitHub Repository (If Not Connected Yet):
-
If there is no existing remote, or you're adding it for the first time, run the following command:
-
git remote add origin https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/GitDemo.git
-
- This command links your local Git project to the GitHub repository.
-
Here :
-
origin: It is the nickname for your GitHub repo (can be anything). -
https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/GitDemo.git: It is the repository URL i.e. actual location of your GitHub repository which we have created in previous tutorial.
-
-
If there is no existing remote, or you're adding it for the first time, run the following command:
-
The commands will show the following output:
-
Other git remote commands:
-
Show All Remotes:
-
Example:
-
git remote
-
-
This lists the names of all connected remotes (e.g.,
origin,upstream).
-
Example:
-
Show Remote URLs:
-
Example:
-
git remote -v
-
- This displays the fetch and push URLs of all remotes.
-
Example:
-
Show Detailed Info About a Remote:
- git remote show <name>
-
Example:
-
git remote show origin
-
- Shows detailed information such as branches, fetch/push URLs, tracking info, and more.
-
Add a new remote:
-
git remote add <name> <remote-url> -
Example:
-
git remote add origin https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/GitDemo.git
-
-
This sets up a connection named
originto your GitHub repo.
-
-
Rename a remote:
-
git remote rename <old-name> <new-name> -
Example:
-
git remote rename origin gitdemorepo
-
-
This renames the remote from
origintogitdemorepo.
-
-
Remove a remote:
-
git remote remove <name> -
Example:
-
git remote remove origin
-
-
This removes the remote connection named
origin.
-
-
Change the URL of an Existing Remote:
-
git remote set-url <name> <new-url> -
Exmaple:
-
git remote set-url origin https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/NewRepo.git
-
-
This updates the URL of the existing remote named
origin.
-
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.