Queue Interface in Java
Introduction
- Queue is the child interface of the Collection interface.
-
It is present in the
java.utilpackage. - It was introduced in JDK 1.5 version.
-
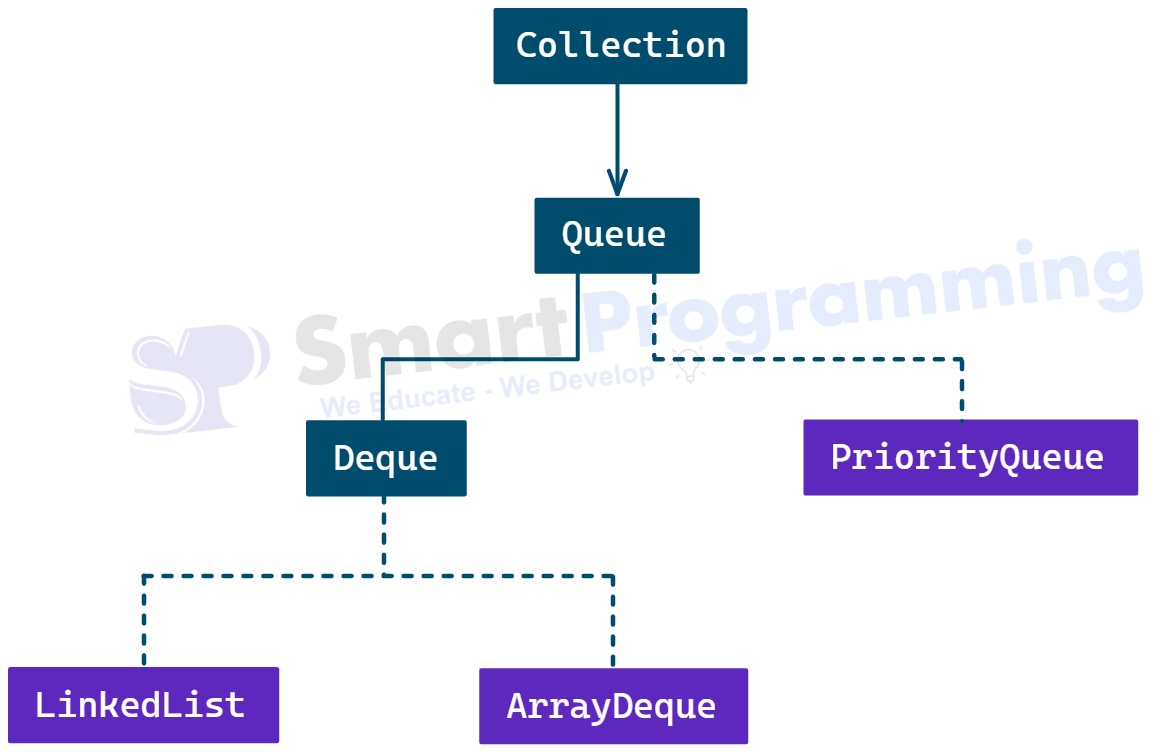
Hierarchy of Queue Interface:
-
- Queue is used to hold elements prior to processing. It follows the FIFO (First-In-First-Out) order, where the element inserted first is removed first.
-
Syntax :-
package java.util; public interface Queue<E> extends Collection{ // Methods (abstract) }
Methods of Queue Interface:
-
Below are the methods defined specifically in the
Queueinterface:
| Sr. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | boolean add(E e) |
Inserts the specified element into the queue.
If the queue is full, this method throws an IllegalStateException.
|
| 2 | boolean offer(E e) |
Inserts the specified element into the queue if possible.
Returns true on success and false if the queue is full.
|
| 3 | E remove() |
Retrieves and removes the head of the queue.
Throws NoSuchElementException if the queue is empty.
|
| 4 | E poll() |
Retrieves and removes the head of the queue, or returns null if the queue is empty.
|
| 5 | E element() |
Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue.
Throws NoSuchElementException if the queue is empty.
|
| 6 | E peek() |
Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue,
or returns null if the queue is empty.
|
Note :
-
The
Queueinterface methods are designed to handle both normal and exceptional cases. Methods likeadd()andremove()throw exceptions, whileoffer()andpoll()return special values (falseornull). -
The
Queueinterface follows the FIFO (First-In-First-Out) order, but some implementations likePriorityQueueorder elements based on priority instead.
Program :
-
In the below program, we are using
Queueimplemented class i.e.LinkedList. -
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class QueueDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // Adding elements queue.add("Amit"); queue.add("Deepak"); queue.add("Kamal"); queue.add("Rahul"); queue.add("Ravi"); // Displaying the queue System.out.println("Initial Queue: " + queue); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Accessing the head element System.out.println("Head element (peek): " + queue.peek()); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Removing elements System.out.println("Removed element (poll): " + queue.poll()); System.out.println("Queue after poll: " + queue); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Adding another element using offer() queue.offer("Mohit"); System.out.println("Queue after offer: " + queue); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Iterating through the queue System.out.println("Iterating the Queue elements:"); for (String name : queue) { System.out.println(name); } } }Output:
Initial Queue: [Amit, Deepak, Kamal, Rahul, Ravi] ------------------------- Head element (peek): Amit ------------------------- Removed element (poll): Amit Queue after poll: [Deepak, Kamal, Rahul, Ravi] ------------------------- Queue after offer: [Deepak, Kamal, Rahul, Ravi, Mohit] ------------------------- Iterating the Queue elements: Deepak Kamal Rahul Ravi Mohit
Properties of Queue Interface:
- Queue is an ordered data structure that stores elements in a sequence for processing.
- It generally follows the FIFO (First-In-First-Out) principle — the element inserted first is removed first.
-
Queue does not provide random access like
List; elements are accessed only from the head or tail. - Queue can store heterogeneous elements if used without generics, but with generics it stores only homogeneous elements of the specified type.
- Queue allows duplicate elements.
-
Queue allows null values only in certain implementations (like
LinkedList), but some implementations (likePriorityQueue) do not allow null elements. -
Queue does not maintain insertion order strictly in all cases —
for example,
PriorityQueueorders elements according to their priority instead of insertion sequence.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.