PriorityQueue Class in Java
Introduction
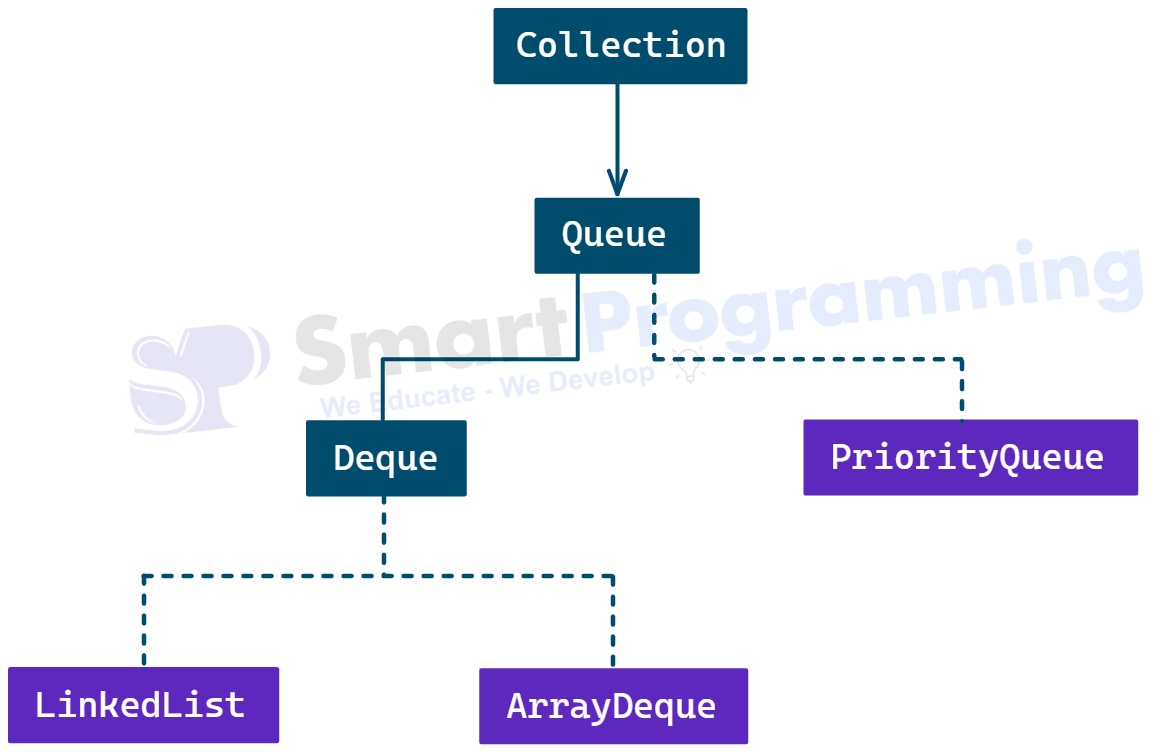
- PriorityQueue is an implemented class of the Queue interface.
-
It is present in the
java.utilpackage. - It was introduced in JDK 1.5 version.
-
Hierarchy:
-
-
Syntax :-
package java.util; public class PriorityQueue<E> implements java.io.Serializable { // Constructors // Methods // Fields }
-
PriorityQueue is an unbounded queue that orders its elements according to their natural order or by a provided comparator.

Constructors of PriorityQueue Class
-
Below are the constructors defined in the
PriorityQueueclass:
| Sr. No. | Constructor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PriorityQueue() |
Constructs a PriorityQueue with default initial capacity (11) and natural ordering of elements. |
| 2 | PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) |
Constructs a PriorityQueue with the specified initial capacity and natural ordering of elements. |
| 3 | PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) |
Constructs a PriorityQueue containing the elements of the specified collection, ordered according to their natural ordering. |
| 4 | PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<? super E> comparator) |
Constructs a PriorityQueue with the specified initial capacity and the specified comparator to order the elements. |
Methods of PriorityQueue Class
-
Below are the methods defined specifically in the
PriorityQueueclass:
| Sr. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | boolean offer(E e) |
Adds the specified element to this priority queue. Equivalent to add(), but returns false if element cannot be added. |
| 2 | E poll() |
Retrieves and removes the head (highest priority) of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
| 3 | E peek() |
Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
| 4 | boolean remove(Object o) |
Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue, if it is present. |
| 5 | boolean contains(Object o) |
Returns true if this queue contains the specified element. |
Note :
-
PriorityQueueinherits all methods fromQueueandCollectioninterfaces. -
PriorityQueue does not allow
nullelements. -
Elements are ordered either by natural ordering or by a provided
Comparator.
Program :
-
In below program, we are using
PriorityQueuewith unordered integers. -
import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class PriorityQueueDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); // Adding elements in unordered way pq.add(20); pq.add(50); pq.add(30); pq.add(10); pq.add(40); pq.add(70); pq.add(60); System.out.println("PriorityQueue printed directly: " + pq); System.out.println("-------------------------"); System.out.println("Polling elements (retrieved in sorted order):"); while(!pq.isEmpty()) { System.out.println(pq.poll()); } } }Output:
PriorityQueue printed directly: [10, 20, 30, 50, 40, 70, 60] ------------------------- Polling elements (retrieved in sorted order): 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
-
Output Explanation:
- Directly printing the PriorityQueue:
- PriorityQueue internally uses a min-heap.
- The heap only guarantees that the smallest element is at the root.
- Other elements are arranged to satisfy the heap property, not fully sorted.
- Hence, when we print it directly, the numbers appear unordered (e.g., [10, 20, 30, 50, 40, 70, 60]).
- Polling elements (poll()):
poll()removes and returns the smallest element each time.- Repeated polling retrieves elements in increasing order.
- Hence the second output shows a sorted sequence: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70.
- Key takeaway:
- Printing the PriorityQueue → heap order (not sorted)
- Polling elements → sorted order according to priority
- Directly printing the PriorityQueue:
Properties of PriorityQueue Class:
- PriorityQueue is a queue-based data structure, which means elements are processed in priority order.
- PriorityQueue can store different data types if generics are not used, but all elements must be mutually comparable to determine priority.
- We can store duplicate elements in the PriorityQueue.
- PriorityQueue does not allow null values.
- PriorityQueue does not follow insertion order; the order of elements depends on their priority.
- PriorityQueue does not maintain full sorting order; only the element with highest priority (smallest for min-heap) is guaranteed at the head.
- PriorityQueue is non-synchronized; not thread-safe for concurrent modifications.
- Elements are retrieved using
poll()orpeek()based on priority. - We can provide a custom comparator to define priority other than natural ordering.
- Internally, PriorityQueue is implemented using a heap (min-heap by default).
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.