One Dimensional Arrays in Java
Introduction
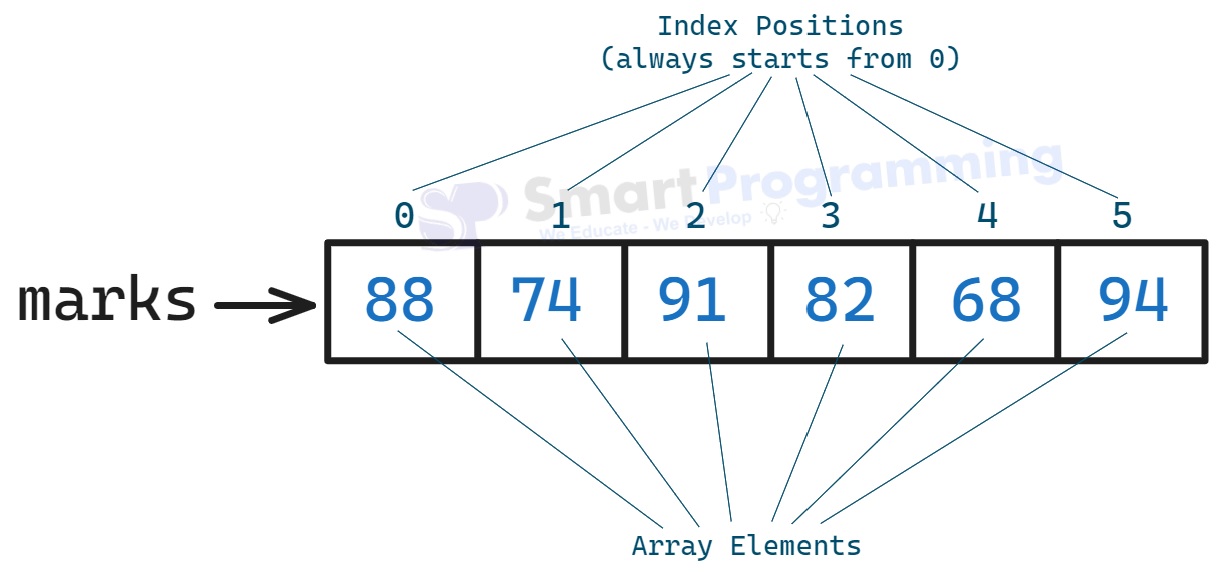
- A one-dimensional array is the simplest form of an array in Java.
- It stores a collection of elements of the same data type in a linear sequence.
- Each element in the array can be accessed using a single index.
- It is often used to represent lists, such as marks of students, prices of products, or names in a list.
-
For example :
-
int[] marks = {88, 74, 91, 82, 68, 94}; -
-
Working with 1D Arrays:
-
To work with 1D arrays in Java, we need to learn the following steps:
- Declare an array - Define the reference of the array with a specific data type.
- Create an array - Allocate memory for the array using the new keyword.
- Initialize an array - Assign values to the elements of the array.
- Retrieve elements of an array - Access array elements using their index.
- We will go through each step with examples below.
1. Declare an array
- Array declaration is the process of defining a variable that can hold multiple values of the same data type.
-
It tells the compiler what type of data the array will store (
int,float,String, etc.). - At this stage, memory is not allocated; only the reference for the array is declared.
-
How to Declare an Array (Commonly Used Syntax):
-
Syntax:
-
dataType[] arrayName;
-
-
Examples:
-
int[] marks; String[] names;
-
-
Syntax:
-
Java also allows some alternate syntaxes to declare a 1D array:
-
Syntax:
-
dataType arrayName[]; dataType []arrayName;
-
-
Examples:
-
int marks[]; int []marks;
-
-
Syntax:
2. Create an Array
- Array creation is the process of allocating memory for the array after it has been declared.
-
This is done using the
newkeyword in Java. - At this stage, a fixed block of memory is reserved to store multiple elements of the specified data type.
- The size of the array must be defined during creation (it cannot be changed later).
-
How to Create an Array:
-
Syntax:
-
arrayName = new dataType[size];
-
-
Examples:
-
marks = new int[6]; names = new String[6];
-
-
Syntax:
NOTE : We can declare and create an array in a single line by combining above 2 steps.
-
Syntax:
-
dataType[] arrayName = new dataType[size];
-
-
Examples:
-
int[] marks = new int[6]; String[] names = new String[6];
-
3. Initialize an Array
- Array initialization is the process of assigning values to the elements of an array.
-
After an array is created, its elements have default values (e.g.,
0forint,0.0forfloat,nullfor objects). -
How to Initialize an Array:
-
Syntax:
-
arrayName[index] = value;
-
-
Examples:
-
marks[0] = 88; marks[1] = 74; marks[2] = 91; marks[3] = 82; marks[4] = 68; marks[5] = 94;
-
-
Syntax:
NOTE : We can declare, create and initialize an array in a single line by combining above 3 steps.
-
Syntax:
-
dataType[] arrayName = {value1, value2, value3, ...};
-
-
Examples:
-
int[] marks = {88, 74, 9182, 68, 94};
-
-
Above syntax is the shorthand of
int[] marks = new int[]{88, 74, 9182, 68, 94};
4. Retrieve elements of an array
- Retrieving array elements means accessing the values stored in the array using their index.
-
Array elements in Java are zero-indexed, so the first element is at index
0and the last element is at indexarray.length - 1. -
Different Ways to Retrieve Elements of an Array
-
Using Index:
-
System.out.println(marks[0]); // Output : 88 System.out.println(marks[3]); // Output : 82
-
-
Using For Loop:
-
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) { System.out.println(marks[i]); }
-
-
Using Enhanced For Loop (For-Each):
-
for(int num : marks) { System.out.println(num); }
-
-
Using
Arrays.toString()(for displaying entire array):-
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers)); // Output: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
-
-
Using Index:
Array Programs:-
-
Program 1:
public class MainApp1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. Declare and create an array of size 6 int[] marks = new int[6]; // 2. Initialize array elements marks[0] = 88; marks[1] = 74; marks[2] = 91; marks[3] = 82; marks[4] = 68; marks[5] = 94; // 3. Access and print array elements using normal for loop (Way 1) System.out.print("Way 1: "); for (int i = 0; i < marks.length; i++) { System.out.print(marks[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); // Move to next line // 4. Access and print array elements using for-each loop (Way 2) System.out.print("Way 2: "); for (int no : marks) { System.out.print(no + " "); } System.out.println(); // Move to next line } }Output:
Way 1: 88 74 91 82 68 94 Way 2: 88 74 91 82 68 94
-
Points to note:
- We have accessed the array elements in 2 ways, i.e., using normal for loop and for-each loop. But for-each loop is preferred as it is simple and easy to understand.
- Declaring and creating array like above is lengthy. We can also declare, create, and initialize the array in a single line using shorthand notation as shown in Program 2 below.
-
Points to note:
-
Program 2:
public class MainApp2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. Declare and create an array using shorthand notation // This automatically initializes the array with the given values int[] marks = {88, 74, 91, 82, 68, 94}; // 2. Access and print array elements using a for-each loop // The variable 'no' takes the value of each element sequentially System.out.print("Marks are: "); for (int no : marks) { System.out.print(no + " "); // Print each element } } }Output:
Marks are: 88 74 91 82 68 94
-
Points to note:
- In this program, we have declared, created, and initialized the array in a single line using shorthand notation.
- We have accessed the array elements using for-each loop, which is the more preferred way.
-
Points to note:
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



