Matrix Array in Java
Introduction
- A Matrix Array is a type of 2D array which stores data in a rows x columns format, just like a table or grid.
- It is used to perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and finding determinants.
-
For example :
-
int[][] matrixArr = { {10, 20, 30}, {40, 50, 60}, {70, 80, 90} }; -
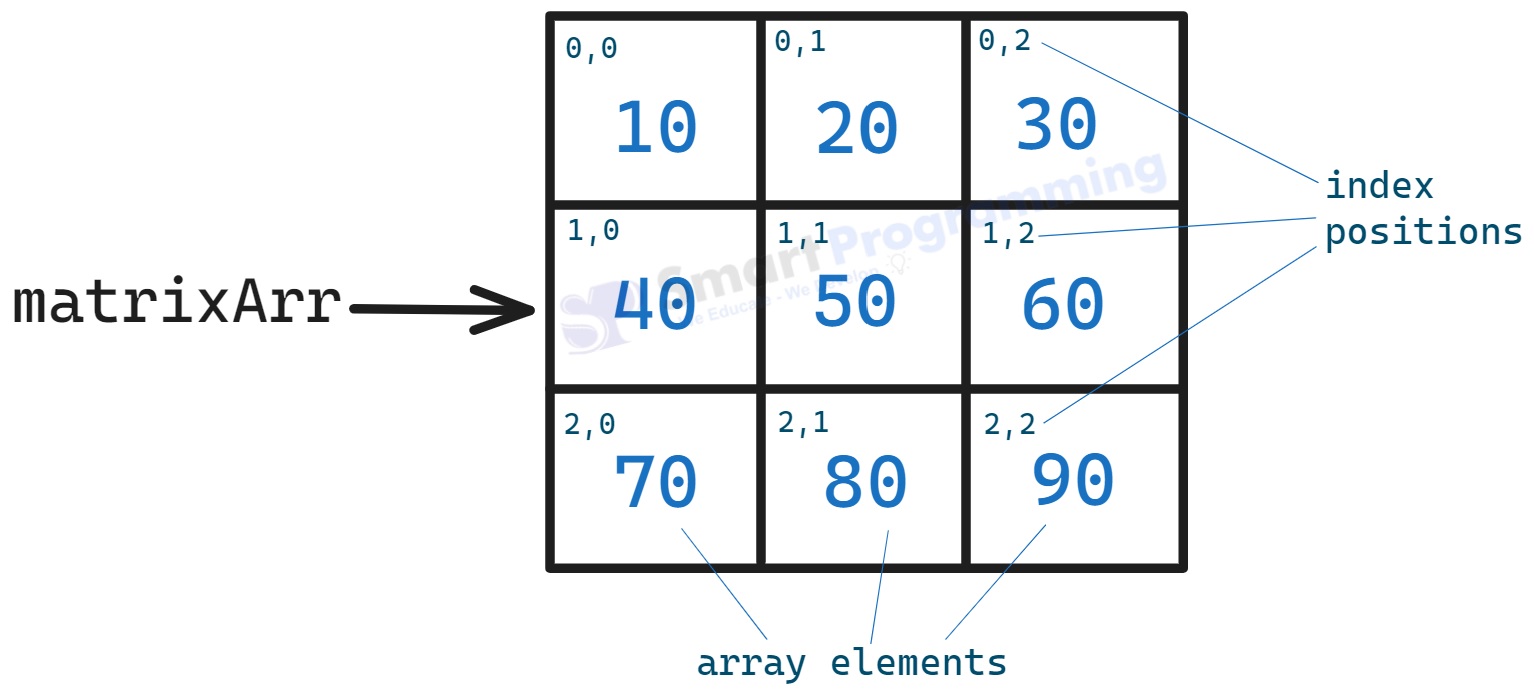
-
-
Points to Remember:
-
Matrix array stores only numeric values (
int,float,double), not Strings, Objects, etc.- Because matrix operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and other calculations only make sense with numbers.
- Storing Strings or Objects would prevent performing mathematical operations.
-
Matrix array can have any number of rows, but every row must have the same number of columns.
-
Example:
int[][] matrix = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6} };
-
Example:
-
Matrix array stores only numeric values (
Working with Matrix Arrays:
-
To work with matrix arrays in Java, we need to follow these steps:
- Declare an array – Define the reference of the array with a specific data type.
-
Create an array – Allocate memory for the array using the
newkeyword. - Initialize an array – Assign values to the elements of the array.
- Retrieve elements of an array – Access array elements using their row and column index.
- We will go through each step with examples below.
1. Declare Matrix Array
-
We can declare a matrix array in the same way as a 2D array.
-
Syntax:
dataType[][] arrayName; -
Example:
int[][] numbers;
-
Syntax:
2. Create Matrix Array
-
We can create a matrix array by specifying rows and columns:
-
Syntax:
arrayName = new dataType[rows][columns]; -
Example:
numbers = new int[2][3];
-
Syntax:
NOTE : We can declare and create a matrix array in a single line.
-
Syntax:
dataType[][] arrayName = new dataType[rows][columns]; -
Example:
int[][] numbers = new int[2][3];
3. Initialize Matrix Array
- Array initialization means assigning values to matrix array.
-
After creation, all the index positions have default values (e.g.,
0forint,0.0forfloatetc). -
We can initialize matrix array elements as below:
-
Syntax:
arrayName[rowIndex][columnIndex] = value; -
Example:
int[][] numbers = new int[2][3]; numbers[0][0] = 10; numbers[0][1] = 20; numbers[0][2] = 30; numbers[1][0] = 40; numbers[1][1] = 50; numbers[1][2] = 60;
-
Syntax:
NOTE : We can declare, create, and initialize a matrix array in a single line.
-
Syntax:
dataType[][] arrayName = { {value1, value2, value3, ...}, {value4, value5, value6, ...}, ... }; -
Example:
int[][] numbers = { {10, 20, 30}, {40, 50, 60} };
4. Retrieve Elements of Matrix Array
-
Ways to retrieve elements from matrix array:
-
Using Nested For Loop:
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < numbers[i].length; j++) { System.out.println(numbers[i][j]); } } -
Using Enhanced For Loop (For-Each):
for(int[] row : numbers) { for(int num : row) { System.out.println(num); } }
-
Using Nested For Loop:
Extra Notes:
numbers.length→ gives the number of rows.numbers[i].length→ gives the number of columns in the i-th row.- Matrix arrays in Java are stored as arrays of arrays, so rows can have different lengths (called a jagged array).
Matrix Array Programs:-
-
Program 1:
public class MainApp1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. Declare, create, and initialize matrix array in a single line int[][] numbers = { {10, 20, 30}, {40, 50, 60} }; // 2. Access and print array elements using nested for-each loop System.out.println("Numbers are:"); for (int[] row : numbers) { for (int num : row) { System.out.print(num + " "); } System.out.println(); // Move to next row } } }Output:
Numbers are: 10 20 30 40 50 60
-
Program 2 (Addition of 2 Matrix Array):
public class MatrixAddition { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. Declare and initialize two 2x3 matrices int[][] matrix1 = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6} }; int[][] matrix2 = { {7, 8, 9}, {10, 11, 12} }; // 2. Create a result matrix of the same size int[][] sum = new int[2][3]; // 3. Perform matrix addition using nested for loop for (int i = 0; i < matrix1.length; i++) // rows { for (int j = 0; j < matrix1[i].length; j++) // columns { sum[i][j] = matrix1[i][j] + matrix2[i][j]; } } // 4. Print the result matrix System.out.println("Result of Matrix Addition:"); for (int i = 0; i < sum.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < sum[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(sum[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); // Move to next row } } }Output:
Result of Matrix Addition: 8 10 12 14 16 18
-
Points to note:
- We created two Matrix Arrays and a third array to store the sum.
- Using nested for loops, we added corresponding elements of both matrices and stored them in the result matrix.
-
Points to note:
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



