Exception in Java
Introduction
- An Exception is an unwanted event that occurs during the execution of a program and disrupts the normal flow of instructions.
- Exceptions usually happen due to problems in the program logic.
-
For Example :
-
IOException
- Occurs when an input/output operation fails.
-
Syntax:
FileReader fr = new FileReader("file.txt"); // May throw IOException
-
ArithmeticException
- Occurs when dividing a number by zero.
-
Syntax:
int result = 10 / 0; // Throws ArithmeticException
-
NullPointerException
- Occurs when calling a method on a null object.
-
Syntax:
String str = null; System.out.println(str.length()); // Throws NullPointerException
-
IOException
- Unlike Errors, exceptions are within the control of the programmer and can be handled in code.
Types of Exceptions in Java
There are two types of Exceptions in Java
-
Checked Exceptions
- Checked Exceptions are those which are checked at compile time.
-
Program won't compile unless they are handled with
try-catchor declared usingthrows. -
Examples :
-
IOException- Input/output operation fails (e.g., file not found).
-
FileReader fr = new FileReader("abc.txt"); // May throw IOException
-
SQLException- Error in database access.
-
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pass); // May throw SQLException
-
-
Unchecked Exceptions
- Unchecked exceptions are those which occur during runtime, not checked by compiler.
- Usually caused by programming mistakes like invalid index, null access, or divide by zero.
-
Examples :
-
ArithmeticException- Divide by zero error.
-
int result = 10 / 0; // Throws ArithmeticException
-
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException- Accessing array index outside valid range.
-
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30}; System.out.println(arr[5]); // Throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
-
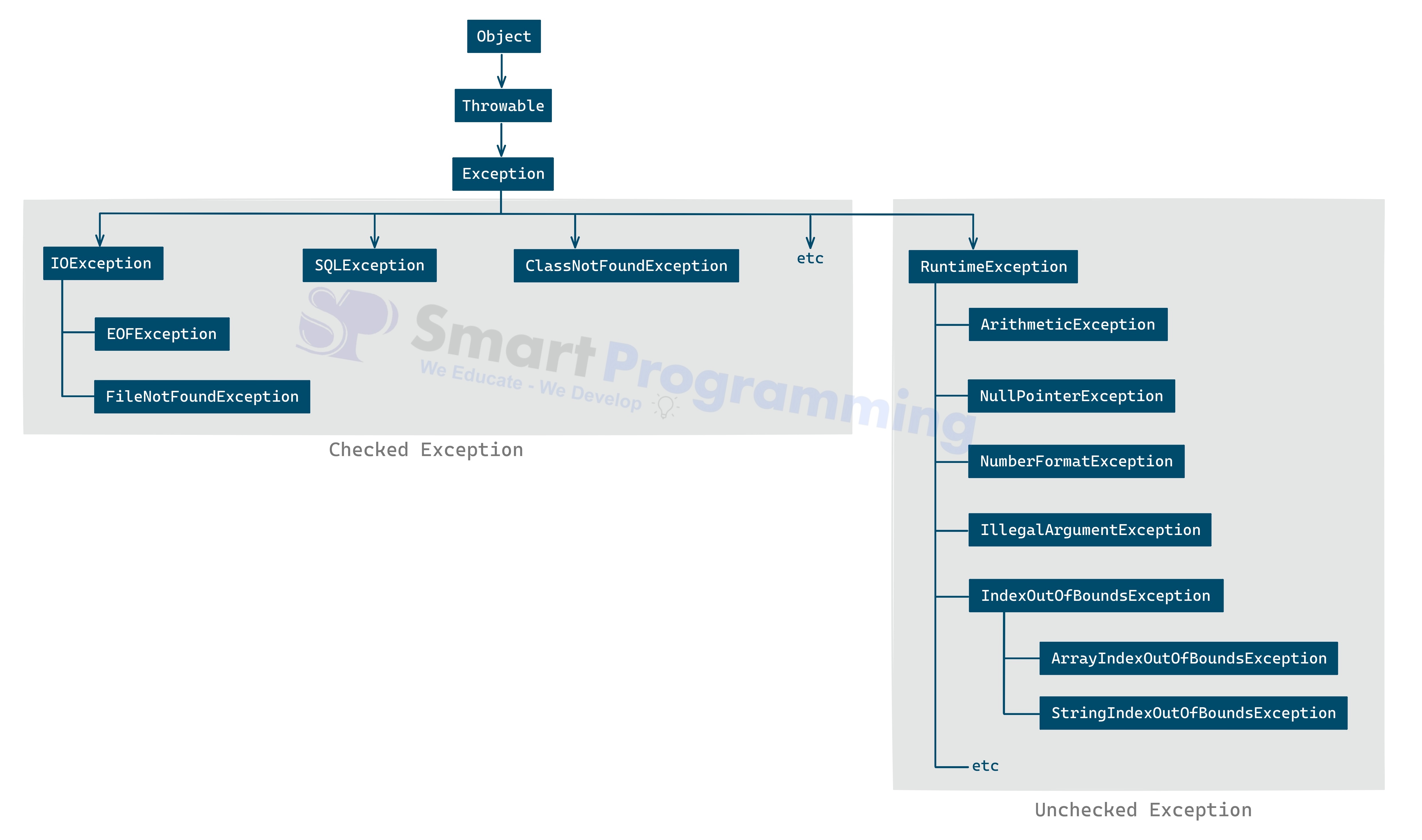
Exception Class Hierarchy
-
Exceptionis the pre-defined class in Java which inherits theThrowableclass. -
Below is the hierarchy of
Exceptionclass in Java.
-
Points to remember:
-
Objectclass is the parent class of all the classes in Java -
Throwableclass is the parent class ofExceptionclass in Java. -
Exceptionclass itself is a checked exception, because it is not a subclass of RuntimeException.
-
What is Exception Handling?
- Exception Handling is the mechanism to handle the exceptions (or runtime errors) so that the normal flow of the program is not disrupted.
-
Need for Exception Handling:
- Prevents program crashes.
- Provides meaningful error messages.
- Separates normal logic from error-handling logic.
- Makes applications more robust and user-friendly.
- Keywords Used in Exception Handling:
-
Points to remember:
-
Technically, the
catchkeyword is used to handle exceptions in Java.-
Other keywords (
try,finally,throw,throws) have different functionalities and do not directly handle exceptions.
-
Other keywords (
-
It is compulsory to handle Checked Exceptions in Java.
- It is not compulsory to handle Unchecked Exceptions, but it is a best practice to handle both (Checked and Unchecked) for making applications more stable and user-friendly.
-
Technically, the
-
Difference between Error and Exception in Java:
- Error: Represents serious problems in the JVM that cannot be handled by the program.
- Exception: Represents conditions that can be caught and handled by the program.
- Click Here to read the detailed comparison between Error and Exception in Java.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



