Viewing Differences in Git - git diff
Introduction
-
git diffcommand is used to view changes in files between various states in your Git repository. - It shows the differences between the working directory and the staging area, helping you to review the changes before committing.
- It is useful for code reviews and debugging.
-
When to use
git diff?- To check the differences before committing changes.
- To see changes between specific commits or branches.
- To analyze conflicts during a merge process.
How to use git diff ?
-
View changes in files:
-
git diff
-
-
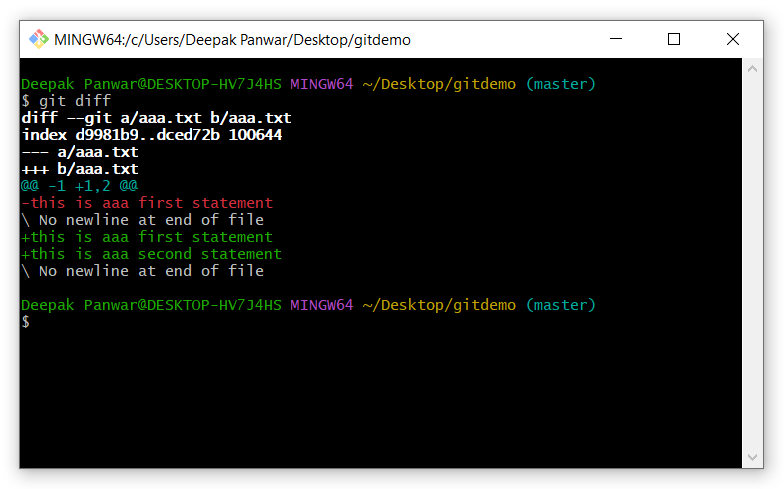
The command will show the following:
-
-
Explanation of the Output:
-
diff --git a/aaa.txt b/aaa.txt
-
This line indicates that the file aaa.txt is being compared.
-
a/aaa.txtThe file version from the staging area (previous state). -
b/aaa.txtThe file version from the working directory (current state).
-
-
This line indicates that the file aaa.txt is being compared.
-
index d9981b9..dced72b 100644
-
d9981b9anddced72bare Git's internal hashes for the content before and after the change. -
100644is the file permission mode.
-
-
--- a/aaa.txt
- This marks the "old" version of the file.
-
+++ b/aaa.txt
- This marks the "new" version of the file.
-
@@ -1 +1,2 @@
-
The
-1means starting at line 1 of the old version. -
The
+1,2means starting at line 1 of the new version, with 2 lines in total.
-
The
-
-this is aaa first statement
-
The line prefixed with
-indicates a line from the old version that was removed.
-
The line prefixed with
-
+this is aaa first statement
+this is aaa second statement-
The lines prefixed with
+indicate lines added in the new version.
-
The lines prefixed with
-
\ No newline at end of file
- This message means that the file does not end with a newline character.
-
diff --git a/aaa.txt b/aaa.txt
Different ways to use git diff ?
-
View Unstaged Changes:
-
git diff - Shows changes between the working directory and the staging area.
- Useful to check modifications before staging.
-
-
View Staged Changes:
-
git diff --cached - Shows differences between the staging area and the last commit.
- Useful to review changes before committing.
-
-
Compare Working Directory with Last Commit:
-
git diff HEAD - Displays all changes since the last commit.
- Useful to see all modifications, whether staged or not.
-
-
Compare Specific Commits:
-
git diff commit1 commit2 - Compares the differences between two commits.
- Useful for tracking changes over time.
-
-
View Changes for a Specific File:
-
git diff filename.txt - Shows modifications made to a specific file.
- Useful for focused code reviews.
-
-
Compare Staged and Unstaged Changes for a File:
-
git diff filename.txt
git diff --cached filename.txt - Useful to compare what's modified but not staged vs. staged but not yet committed.
-
-
Show Changes in a Specific Commit:
-
git diff commit-hash - Displays changes introduced by a specific commit.
- Useful to understand the impact of a particular commit.
-
-
Compare Changes Between Branches:
-
git diff branch1 branch2 - Compares the differences between two branches.
- Useful to check what will be merged or needs resolution.
-
-
Ignore Whitespace Changes:
-
git diff -w - Ignores whitespace differences, focusing only on actual code changes.
- Useful for cleaner comparisons.
-
-
Show Summary of Changes:
-
git diff --stat - Shows a summary of the number of files changed, and lines added/removed.
- Ideal for a quick overview of modifications.
-
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.