Java Hello Program Deep Explanation
Simple Java Hello Program
In last tutorial, we have deeply explained the Structure of Java Hello Program. Now, below is the simple Java Hello Program.
MainApp.java
public class MainApp
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello Deepak");
}
}In this example, we have a class named MainApp, and within this class, there is a main method. The method prints "Hello Deepak...!!" to the console.
Breaking Down the program as below:-
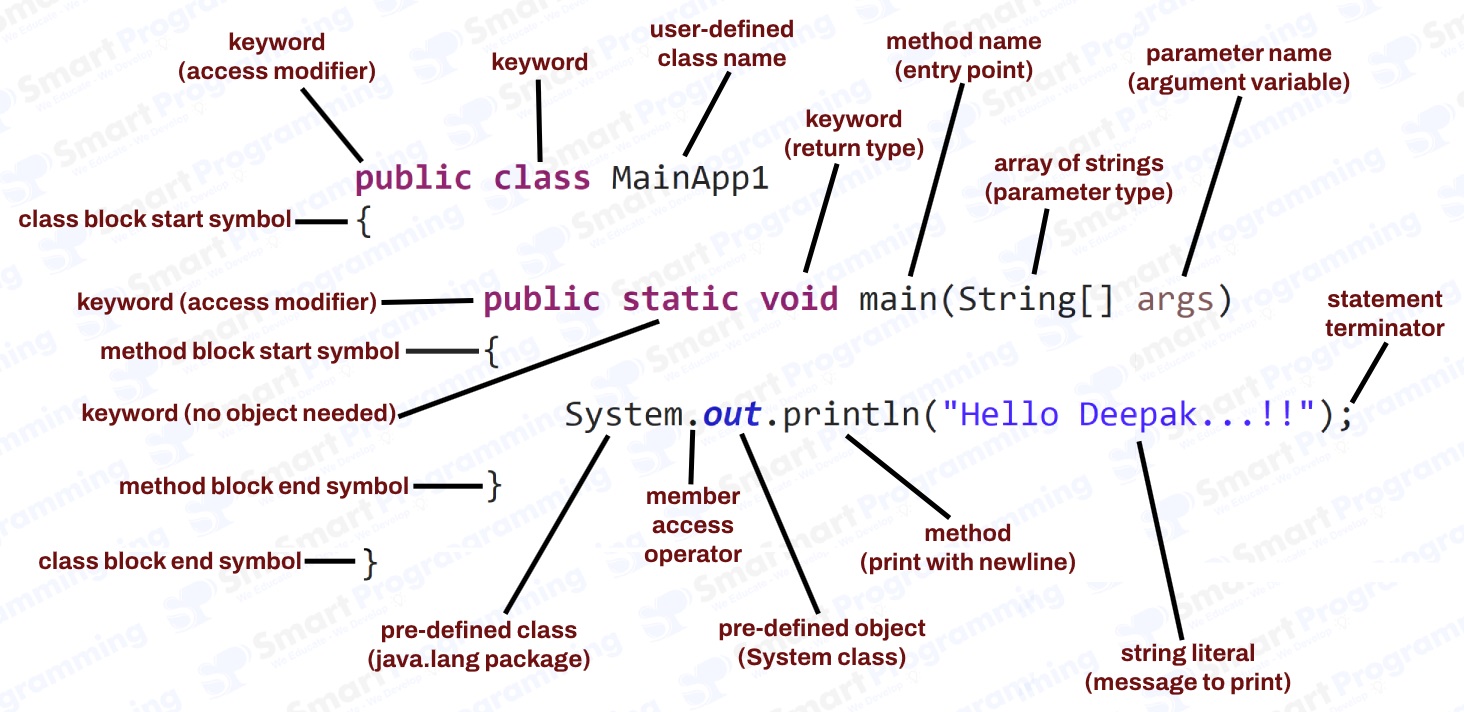
-
1. public (Keyword - Access Modifier)
- The "public access modifier keyword" declares that the MainApp class is accessible from anywhere in the program (other packages are also included) and JVM can invoke it from outside the class.
- Note that when a class is declared as public, it must have the same name as the file name (in this case, MainApp.java).
-
2. class (Keyword)
- The "class keyword" is used to define a class in Java, which acts as a blueprint for creating objects.
-
The class can contain :-
- Variables: Store data or attributes of the class.
- Constructors: Initialize the object’s state.
- Methods: Define the behavior or actions of the class.
-
3. MainApp (User-Defined Class Name)
- The "MainApp" is the user-defined class name which contains the overall program.
- The class must follows the Java naming conventions (CamelCase starting with an uppercase letter).
- The "MainApp" class acts as the entry point of the program because it contains the main method.
-
4. { (Class Opening Curly Brace)
- Here "{" denotes the beginning of the class definition.
- Every class body is enclosed in curly braces.
-
5. public (Keyword - Access Modifier)
- The "public access modifier keyword" here makes the main method accessible to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) so it can execute the program.
-
6. static (Keyword)
-
The "static keyword" denotes that the main method belongs to the class rather than an instance of the class.
- It means that the main method is called without creating an object of the MainApp class.
-
The "static keyword" denotes that the main method belongs to the class rather than an instance of the class.
-
7. void (Keyword - Return Type)
- The "void return-type keyword" indicates that the main method does not return any value.
- Since the program’s execution does not require any return value from the main method, it is declared void.
-
8. main (Pre-Defined Method)
- The "main pre-defined method" is an entry point of the program from where execution begins.
- The JVM looks for this specific method (main() method) to start the program. If there is no main() method then JVM will not start the program execution.
-
9. String[] (Parameter Type - Array of Strings)
- The "String[] parameter type" is used for Command-line Arguments. It holds the arguments passed to the program when it is executed via the command line.
-
For example: If we run
java MainApp Hello Deepak, the array will contain:- String[0] = "Hello"
- String[1] = "Deepak"
-
10. args (Parameter Name - Argunment Variable)
- The "args" is the user-defined variable name for the String[] parameter.
- "args" is the short name for arguments, but can be renamed to any valid identifier (e.g., data or parameters).
- It is used to hold the command-line arguments passed to the program.
-
11. { (Method Opening Curly Brace)
- Here "{" denotes the beginning of the main method body.
-
12. System (Pre-Defined Class Name)
-
"System" is the built-in Java class from
java.langpackage. - It provides access to system-level functionality, such as input/output streams, properties, and environment variables.
-
It contains:
-
in:Standard input stream (e.g., keyboard input). -
out:Standard output stream (e.g., console output). -
err:Standard error stream (e.g., error messages).
-
-
"System" is the built-in Java class from
-
13. . (Member Access Operator)
- "." is the member access operator which is used to access fields, methods and nested classes of a class or an object.
- For example: System.out accesses the out field of the System class.
-
It contains:
-
in:Standard input stream (e.g., keyboard input). -
out:Standard output stream (e.g., console output). -
err:Standard error stream (e.g., error messages).
-
-
14. out (Pre-Defined Object)
- "out" is the static member (field or property) of "System" class that represents the standard output stream (usually the console).
- It is used to print the data like strings, numbers or objects to the console.
-
15. println (Pre-Defined Method)
- "println" is the pre-defined method of "PrintStream" class (referenced by System.out).
- It prints the given text or data to the console and moves the cursor to a new line.
-
16. "Hello Deepak" (String Literal)
- "Hello Deepak" is the sequence of characters enclosed in double quotes.
- The text Hello Deepak is passed as an argument to the println method and will be displayed in the console.
-
16. ; [Semicolon] (Statement Terminator)
- ";" marks the end of a statement in Java. Every executable statement must be terminated with a semicolon.
-
17. } (Method Closing Curly Brace:)
- Here "}" marks the end of the main method body.
-
18. } (Class Closing Curly Brace)
- Here "}" marks the end of the class definition.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



