Types of Inheritance in Java
Introduction
- Inheritance in Java means one class can use the properties (like variables and methods) of another class.
- It is the fundamental concept of OOP's which helps to reuse code.
- It creates a parent-child relationship, where the parent is called the superclass and the child is called the subclass.
- Click here to read more about Inheritance in Java.
-
There are 5 types of Inheritance in Java:
- Single Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance (not supported directly)
- Hybrid Inheritance (not supported directly)
Single Inheritance:
- Single level inheritance is a type of inheritance in which a child class inherits directly from a single parent class.
- It allows the child class to reuse the fields and methods of the parent class.
-
Syntax:
class ParentClass { // Parent class code } class ChildClass extends ParentClass { // Child class code }

-
Program example:
// Parent class class BankAccount { void accountType() { System.out.println("This is a general bank account."); } } // Child class class SavingsAccount extends BankAccount { void interestRate() { System.out.println("Savings account offers 4% interest."); } } // Main class public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { SavingsAccount sa = new SavingsAccount(); sa.accountType(); // Inherited method sa.interestRate(); // Specific method } }Output:
This is a general bank account. Savings account offers 4% interest.
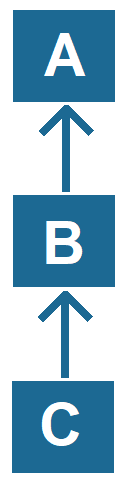
Multilevel Inheritance:
- Multilevel inheritance is a type of inheritance where a class inherits from a child class, making a chain of inheritance.
- Here, a class acts as a parent for another class, which in turn acts as a parent for a third class.
- This forms a hierarchy of classes connected through inheritance.
-
Syntax:
class Grandparent { // code } class Parent extends Grandparent { // code } class Child extends Parent { // code }
-
Program example:
// Grandparent class class Animal { void eat() { System.out.println("Animal is eating."); } } // Parent class class Dog extends Animal { void bark() { System.out.println("Dog is barking."); } } // Child class class Puppy extends Dog { void weep() { System.out.println("Puppy is weeping."); } } public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { Puppy p = new Puppy(); p.eat(); // From Animal p.bark(); // From Dog p.weep(); // Own method } }Output:
Animal is eating. Dog is barking. Puppy is weeping.
-
Important Points to Remember:
- Multilevel inheritance represents a class hierarchy with more than two levels.
- The child class inherits properties from its parent class and all ancestor classes.
- Supports code reuse across multiple levels.
- Helps model real-world hierarchical relationships.
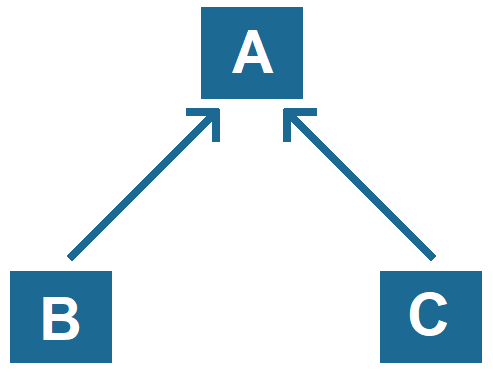
Hierarchical Inheritance:
- Hierarchical inheritance is a type of inheritance where multiple child classes inherit from a single parent class.
- It allows multiple subclasses to share the properties and behaviors of the same parent class.
- This type of inheritance is useful for creating a common base class for multiple classes.
-
Syntax:
class Parent { // Parent class code } class Child1 extends Parent { // Child1 specific code } class Child2 extends Parent { // Child2 specific code }
-
Program example:
// Parent class class Vehicle { void fuelType() { System.out.println("Uses fuel."); } } // First child class class Car extends Vehicle { void wheels() { System.out.println("Car has 4 wheels."); } } // Second child class class Bike extends Vehicle { void handleType() { System.out.println("Bike has a handlebar."); } } public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { Car c = new Car(); c.fuelType(); // Inherited from Vehicle c.wheels(); // Car specific Bike b = new Bike(); b.fuelType(); // Inherited from Vehicle b.handleType(); // Bike specific } }Output:
Uses fuel. Car has 4 wheels. Uses fuel. Bike has a handlebar.
-
Important Points to Remember:
- Hierarchical inheritance allows code reuse through a shared parent class.
- Each subclass gets its own copy of the parent class’s properties and methods.
- It promotes loose coupling by separating shared logic into a base class.
- It's useful when multiple classes share common behavior and properties.
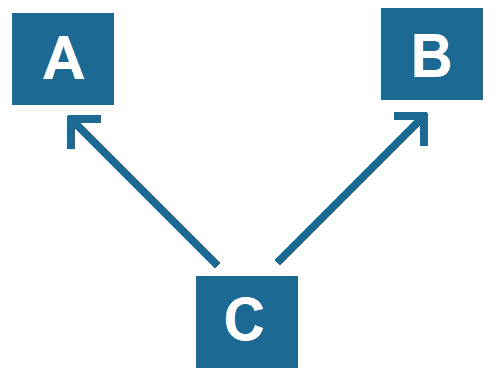
Multiple Inheritance:
Note: Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes to avoid ambiguity problems (commonly known as the "Diamond Problem"). However, it can be achieved using interfaces.
- Multiple inheritance refers to a feature where a class can inherit features (methods and fields) from more than one parent class.
- Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes directly, but it supports it through interfaces.
- This prevents conflicts and ambiguity caused by the Diamond Problem.
-
Syntax using interfaces:
interface A { void methodA(); } interface B { void methodB(); } class C implements A, B { public void methodA() { System.out.println("Method from interface A"); } public void methodB() { System.out.println("Method from interface B"); } }
-
Program example (using interfaces):
// Interface A interface A { void displayA(); } // Interface B interface B { void displayB(); } // Class C implementing both interfaces class C implements A, B { public void displayA() { System.out.println("Display from interface A"); } public void displayB() { System.out.println("Display from interface B"); } } public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { C obj = new C(); obj.displayA(); obj.displayB(); } }Output:
Display from interface A Display from interface B
-
Important Points to Remember:
- Java classes cannot extend more than one class at a time.
- Multiple inheritance is achieved using interfaces in Java.
- This design avoids ambiguity and promotes clean architecture.
- Interfaces define abstract behavior that multiple classes can implement.
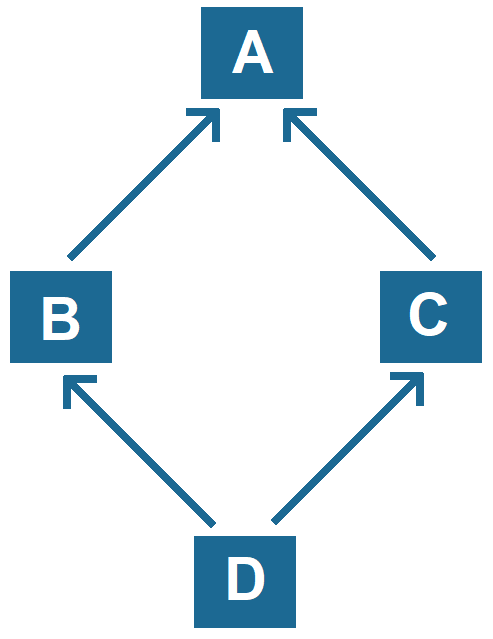
Hybrid Inheritance:
Note: Java does not support hybrid inheritance with classes directly because it may lead to ambiguity. However, it can be achieved using interfaces to simulate hybrid behavior.
- Hybrid inheritance is a combination of two or more types of inheritance (e.g., single, multiple, multilevel).
- It represents a scenario where different inheritance types are combined to form a complex hierarchy.
- Java does not support hybrid inheritance with classes due to ambiguity issues but supports it through interfaces.
-
Syntax using interfaces and a class:
interface A { void methodA(); } interface B { void methodB(); } class C { void methodC() { System.out.println("Method from class C"); } } // Class D inherits class C and implements A and B class D extends C implements A, B { public void methodA() { System.out.println("Method from interface A"); } public void methodB() { System.out.println("Method from interface B"); } }
-
Program example (using interfaces and class):
// Interface A interface A { void showA(); } // Interface B interface B { void showB(); } // Class C class C { void showC() { System.out.println("Show from class C"); } } // Class D: extends C and implements A and B class D extends C implements A, B { public void showA() { System.out.println("Show from interface A"); } public void showB() { System.out.println("Show from interface B"); } } // Main class public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { D obj = new D(); obj.showA(); obj.showB(); obj.showC(); } }Output:
Show from interface A Show from interface B Show from class C
-
Important Points to Remember:
- Hybrid inheritance combines multiple types of inheritance to represent more complex relationships.
- Java does not support hybrid inheritance with classes directly.
- It can be implemented safely using interfaces to avoid ambiguity.
- Helps in designing systems with multiple traits and layered behaviors.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



