Two Pointers Technique
Introduction
-
The Two Pointers Technique is a problem-solving strategy where we use two variables
(
pointers) to traverse anarray,stringorlinked listfrom different directions or at different speeds. -
Its goal is to reduce time complexity by avoiding nested loops and processing
data in
O(n)instead ofO(n²). -
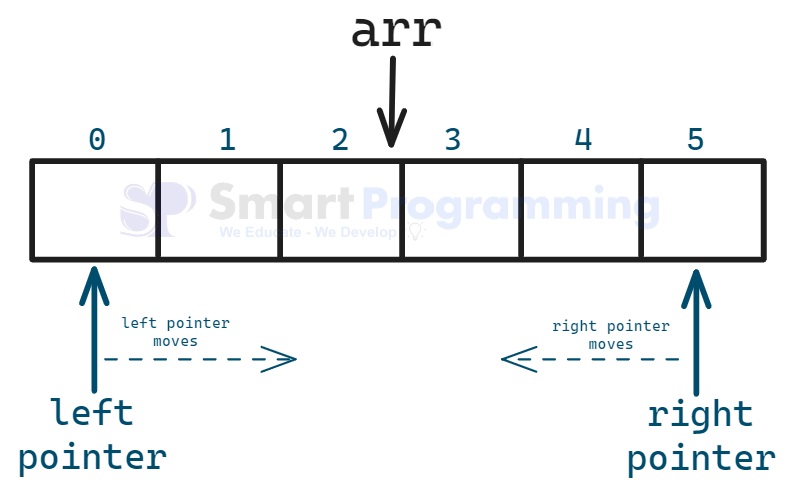
Types of Movement:
1. Opposite Direction :
In this approach, one pointer starts at the beginning of the array and the other at the end. They move towards each other based on certain conditions.
 2. Same Direction :
2. Same Direction :
Here, both pointers start at the beginning of the array and move forward at different speeds or steps to find subarrays or pairs.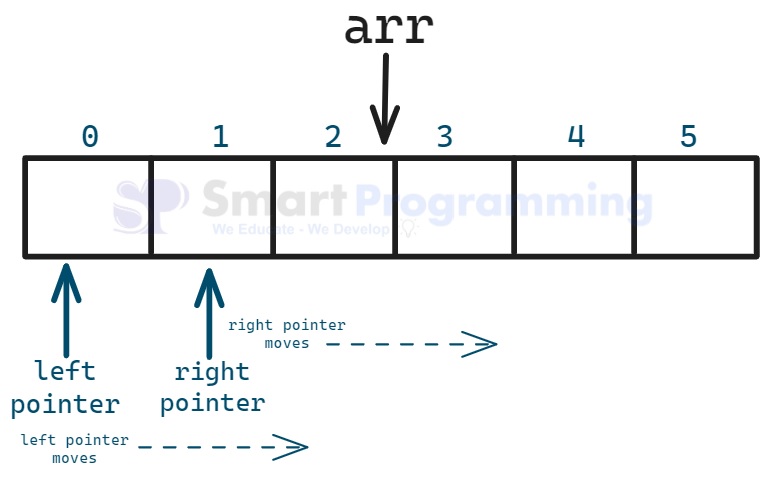 3. Independent Direction :
3. Independent Direction :
In this type, both pointers can move in any direction independently based on specific conditions.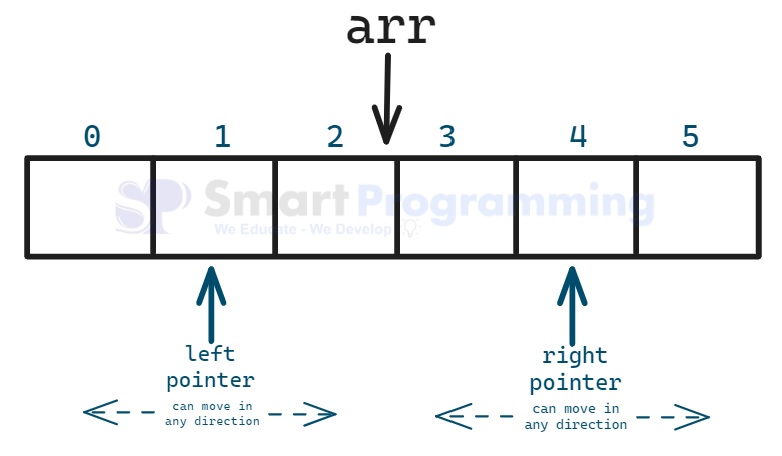
-
Advantages:
-
Better Time Complexity: Often reduces from
O(n²)→O(n)orO(n log n). -
Space Efficient: Works with constant extra space (
O(1)). - Simpler Logic: Easy to implement once we understand the pattern.
-
Versatile: Can be applied to
arrays,strings, andlinked lists.
-
Better Time Complexity: Often reduces from
Programs:-
-
Program 1: Two Sum in Sorted Array (Using Opposite Direction)
public class MainApp1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {2, 3, 4, 7, 11, 15}; int target = 10; int left = 0, right = arr.length - 1; boolean found = false; while (left < right) { int sum = arr[left] + arr[right]; if (sum == target) { System.out.println("Pair found at "+left+" and "+right+" index positions"); found = true; break; } else if (sum < target) { left++; // Move left pointer forward } else { right--; // Move right pointer backward } } if (!found) System.out.println("No pair found"); } }Output:
Pair found at 1 and 3 index positions
-
Program 2: Remove duplicates from sorted array (Using Same Direction)
public class MainApp2 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5}; int n = nums.length; int left = 0; // last unique element position // Two pointers: right scans, left writes unique values for (int right = 1; right < n; right++) { if (nums[left] != nums[right]) { left++; // move left forward nums[left] = nums[right]; // copy unique element } } // Print unique elements (from index 0 to left) System.out.print("Array after removing duplicates: "); for (int i = 0; i <= left; i++) { System.out.print(nums[i] + " "); } } }Output:
Array after removing duplicates: 1 2 3 4 5
Two-Pointers Technique Task:
Try to solve the following problems using the Two Pointers Technique:
- WAP to Move Zeros to End of an Array
- WAP to Find Triplet with Given Sum in a Sorted Array
- WAP to Check if an Array is Palindrome
- WAP to Find Maximum Water Container
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.